How Do You Make Money On A Put Options
What is a Call Option?
A call option, commonly referred to as a "call," is a class of a derivatives contract that gives the phone call option buyer the correct, just not the obligation, to buy a stock or other financial instrument at a specific price – the strike price of the choice – within a specified time frame. The seller of the option is obligated to sell the security to the buyer if the latter decides to exercise their option to brand a buy. The buyer of the option can exercise the option at whatever time prior to a specified expiration date. The expiration engagement may be three months, six months, or even 1 year in the future.
The seller receives the purchase price for the pick, which is based on how close the option strike toll is to the price of the underlying security at the time the option is purchased, and on how long a period of time remains till the option'southward expiration date. In other words, the price of the option is based on how likely, or unlikely, it is that the pick buyer will have a take a chance to profitably exercise the selection prior to expiration. Unremarkably, options are sold in lots of 100 shares. The heir-apparent of a call choice seeks to make a turn a profit if and when the cost of the underlying nugget increases to a cost higher than the option strike cost.
On the other hand, the seller of the call option hopes that the price of the nugget will decline, or at least never rise as high as the option strike/exercise price before information technology expires, in which case the coin received for selling the option will be pure profit.
If the price of the underlying security does non increase across the strike price prior to expiration, and so information technology will not be profitable for the option buyer to exercise the option, and the option will expire worthless or "out-of-the-money." The buyer will suffer a loss equal to the price paid for the telephone call pick. Alternatively, if the price of the underlying security rises to a higher place the option strike cost, the buyer can profitably exercise the selection.
For example, assume you bought an option on 100 shares of a stock, with an option strike cost of $xxx. Before your option expires, the price of the stock rises from $28 to $40. Then you lot could exercise your right to buy 100 shares of the stock at $30, immediately giving you a $10 per share profit.
Your net profit would exist 100 shares, times $ten a share, minus any purchase price you paid for the choice. In this example, if you had paid $200 for the call option, then your internet profit would be $800 (100 shares 10 $10 per share – $200 = $800).
Buying call options enables investors to invest a small amount of capital to potentially profit from a cost ascent in the underlying security, or to hedge away from positional risks . Small-scale investors apply options to try to turn small amounts of money into big profits, while corporate and institutional investors apply options to increment their marginal revenues and hedge their stock portfolios.
How Exercise Call Options Work?
Since phone call options are derivative instruments, their prices are derived from the price of an underlying security, such as a stock. For case, if a buyer purchases the call pick of ABC at a strike toll of $100 and with an expiration date of December 31, they will have the right to buy 100 shares of the company any time earlier or on Dec 31.
The heir-apparent can likewise sell the options contract to another pick buyer at any time before the expiration date, at the prevailing market price of the contract. If the price of the underlying security remains relatively unchanged or declines, then the value of the choice will pass up equally information technology nears its expiration date.
Investors apply phone call options for the following purposes:
i. Speculation
Call options let their holders to potentially gain profits from a cost ascension in an underlying stock while paying merely a fraction of the cost of buying actual stock shares. They are a leveraged investment that offers potentially unlimited profits and limited losses (the price paid for the option). Due to the loftier degree of leverage, call options are considered high-run a risk investments.
ii. Hedging
Investment banks and other institutions employ call options as hedging instruments. Just like insurance, hedging with an selection reverse your position helps to limit the amount of losses on the underlying instrument should an unforeseen upshot occur. Telephone call options can exist bought and used to hedge curt stock portfolios, or sold to hedge against a pullback in long stock portfolios.
Buying a Phone call Option
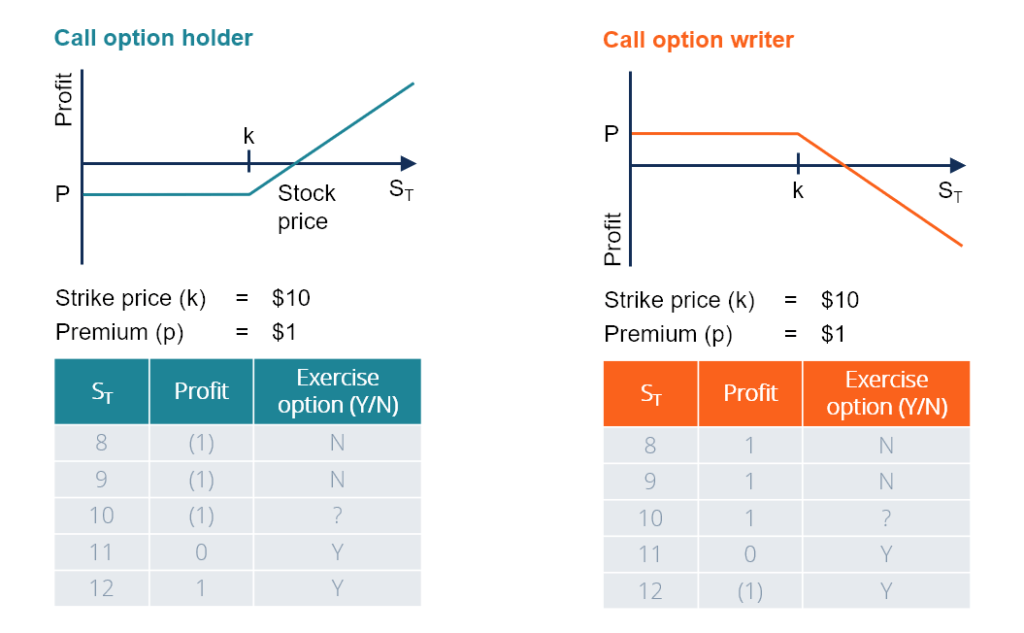
The buyer of a phone call selection is referred to as a holder. The holder purchases a call option with the hope that the price will rise beyond the strike price and earlier the expiration date. The profit earned equals the sale proceeds, minus strike cost, premium, and whatsoever transactional fees associated with the sale. If the price does not increase beyond the strike price, the heir-apparent will non do the selection. The buyer will suffer a loss equal to the premium of the call option.
For example, suppose ABC Company's stock is selling at $40 and a phone call selection contract with a strike price of $40 and an expiry of one month is priced at $2. The buyer is optimistic that the stock price volition rising and pays $200 for one ABC call choice with a strike price of $40. If the stock of ABC increases from $twoscore to $50, the buyer volition receive a gross profit of $yard and a cyberspace profit of $800.
Selling a Call Option
Telephone call option sellers, also known as writers, sell phone call options with the hope that they become worthless at the death engagement. They make money by pocketing the premiums (price) paid to them. Their profit will exist reduced, or may even issue in a cyberspace loss if the option buyer exercises their pick profitably when the underlying security price rises above the choice strike price. Telephone call options are sold in the following two ways:
i. Covered Call Pick
A call option is covered if the seller of the call option actually owns the underlying stock. Selling the call options on these underlying stocks results in additional income, and will starting time any expected declines in the stock price. The option seller is "covered" confronting a loss since in the consequence that the selection buyer exercises their option, the seller can provide the heir-apparent with shares of the stock that he has already purchased at a toll below the strike price of the option. The seller'south profit in owning the underlying stock volition be limited to the stock's ascent to the option strike price but he will be protected against whatsoever bodily loss.
2. Naked Call Option
A naked call option is when an option seller sells a call option without owning the underlying stock. Naked brusk selling of options is considered very risky since there is no limit to how loftier a stock's price tin get and the selection seller is not "covered" against potential losses past owning the underlying stock.
When a call choice heir-apparent exercises his correct, the naked pick seller is obligated to buy the stock at the current market price to provide the shares to the option holder. If the stock toll exceeds the telephone call choice'south strike price, then the difference between the current market price and the strike price represents the loss to the seller. Almost option sellers charge a high fee to compensate for any losses that may occur.
Phone call Option vs. Put Option
A call option and put option are the contrary of each other. A call option is the correct to buy an underlying stock at a predetermined price up until a specified expiration date. On the opposite, a put pick is the right to sell the underlying stock at a predetermined price until a fixed expiry engagement. While a telephone call option buyer has the right (but non obligation) to purchase shares at the strike price before or on the expiry engagement, a put selection buyer has the correct to sell shares at the strike toll.
Related Readings
Give thanks you for reading CFI's guide on Call Options. To continue developing your career every bit a financial professional person, check out the following additional CFI resources:
- Types of Markets – Dealers, Brokers and Exchanges
- Long and Short Positions
- Options Case Study
- Buying on Margins
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/trading-investing/call-option/
Posted by: weesnerforgand57.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Do You Make Money On A Put Options"
Post a Comment